HR Regulatory Compliance
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, organizations must prioritize the protection of employee data while ensuring compliance with relevant regulations. For businesses operating in Ghana, the Ghanaian Data Protection Act, 2012 (Act 843) provides a framework for safeguarding personal data. This article explores the significance of HR regulatory compliance in Ghana and offers strategies for securing employee data.
Understanding HR Regulatory Compliance in Ghana
HR regulatory compliance in Ghana involves adhering to various laws and regulations that govern employment practices and data handling. The Ghanaian Data Protection Act establishes the legal parameters within which organizations must operate when collecting, processing, and storing personal information.
The Act aims to protect the privacy of individuals and promote accountability among data controllers and processors. Non-compliance can result in severe penalties, including fines and damage to an organization’s reputation. Therefore, understanding the implications of the Data Protection Act is critical for HR professionals.
services
The Role of Technology
Technology plays a vital role in HR regulatory compliance and data security. HR software solutions can automate tasks, streamline processes, and enhance data security. For example, cloud-based HR platforms offer robust security features, including encryption, access control, and data backups.

Key Strategies for Compliance and Data Security
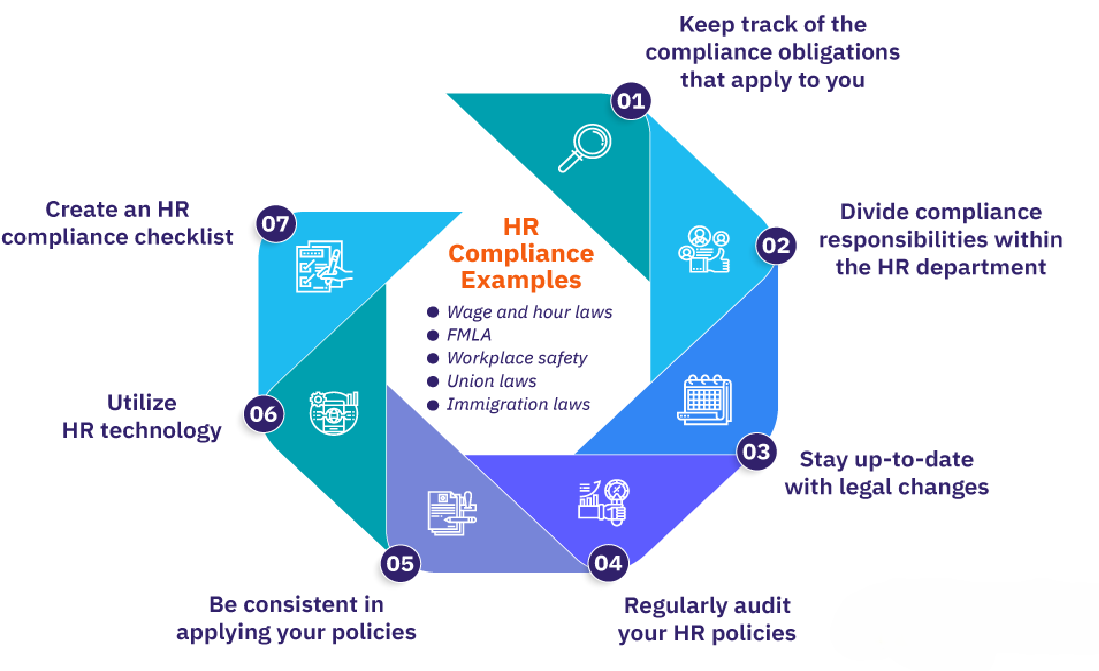
1. Develop a Comprehensive Data Protection Policy
Organizations should establish a data protection policy that outlines how they collect, process, and store employee data. This policy should align with the principles set forth in the Ghanaian Data Protection Act, including obtaining informed consent, ensuring data accuracy, and implementing security measures to protect personal data.
2. Conduct Regular Audits and Assessments
Regular audits are essential for identifying compliance gaps and assessing data security practices. HR departments should evaluate their data handling processes, ensuring they are in line with the Data Protection Act. This proactive approach allows organizations to rectify potential issues before they escalate into legal challenges.
3. Implement Data Minimization Practices
Data minimization is a crucial principle under the Data Protection Act. Organizations should collect only the data necessary for specific employment-related purposes. By limiting data collection, businesses can reduce the risk of exposure in the event of a data breach.
4. Establish Clear Access Controls
Not all employees need access to sensitive data. Implementing clear access control measures ensures that only authorized personnel can view or handle personal information. Regularly reviewing and updating access rights is vital to maintaining data security and minimizing the risk of insider threats.
5. Invest in Employee Training and Awareness
Training employees on data protection regulations and best practices is crucial for maintaining data security. HR should implement ongoing training programs that educate staff about the importance of data privacy, potential threats, and their roles in safeguarding sensitive information. A culture of security awareness empowers employees to protect data proactively.
6. Utilize Technology Solutions
Leveraging technology can significantly enhance data security. Organizations should invest in secure HR software that includes features such as encryption, secure cloud storage, and multi-factor authentication. These tools help mitigate the risk of cyber threats and protect sensitive employee data.
7. Establish a Data Breach Response Plan
Despite best efforts, data breaches can occur. Having a response plan in place ensures organizations can act swiftly in the event of a breach. This plan should outline steps for containment, investigation, and notification of affected individuals, as well as remediation efforts. Regularly testing and updating the response plan is essential for effectiveness.